IPTV The Future of Television
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the way we consume television content has undergone a massive transformation. Traditional television, once the cornerstone of entertainment, is being replaced by more versatile, on-demand, and internet-based services. Among these, Internet Protocol Television, or IPTV, stands out as a revolutionary technology that is redefining the viewing experience. IPTV is not just a new method of delivering television content; it represents a paradigm shift in how media is consumed, offering a level of customization, accessibility, and interaction that was unimaginable a few decades ago.
This comprehensive article explores every facet of IPTV, from its basic principles and types to its advantages over traditional TV and its potential to shape the future of entertainment. As we delve into the details, we will also examine the challenges faced by the IPTV industry, how to choose the right IPTV service, and what the future holds for this exciting technology.
Table of Contents
What is IPTV?
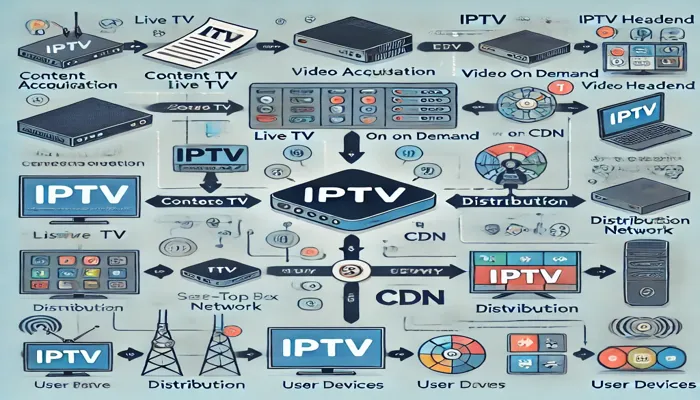
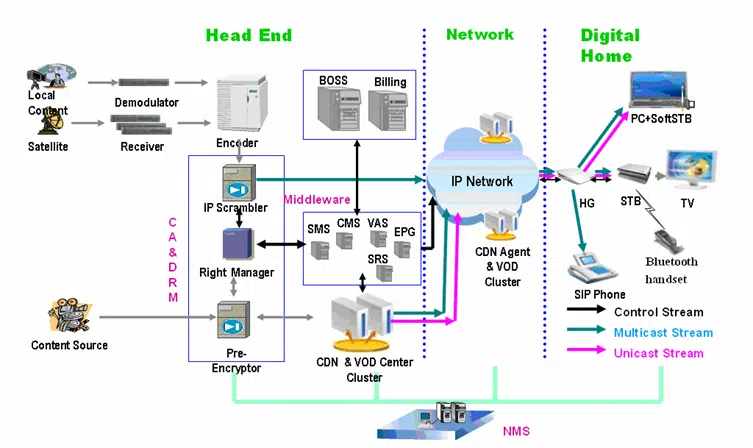
Description: This flowchart illustrates the IPTV process from content acquisition to decoding on the user’s end.
IPTV, or Internet Protocol Television, is a system where television services are delivered using the Internet rather than traditional terrestrial, satellite, or cable television formats. In simpler terms, IPTV allows users to stream live television channels, on-demand videos, and other content directly to their devices using an internet connection.
The Historical Context
To fully appreciate the significance of IPTV, it’s important to understand the historical context of television. The journey of television began with the introduction of broadcast television in the early 20th century. Initially, television was a one-way communication medium where viewers could only watch what was being broadcast at that time. There was no flexibility in terms of choosing what to watch or when to watch it.
The advent of cable television in the 1970s and 1980s brought more options to viewers. Cable TV allowed for a greater variety of channels, including specialty channels dedicated to sports, movies, and news. However, the viewing experience was still largely dictated by the broadcasters’ schedules.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the emergence of digital television, which improved picture quality and allowed for the inclusion of more channels. However, it wasn’t until the widespread adoption of the internet that a true revolution in television consumption began. IPTV, which emerged in the early 2000s, leveraged the power of the internet to provide a more flexible and personalized viewing experience.
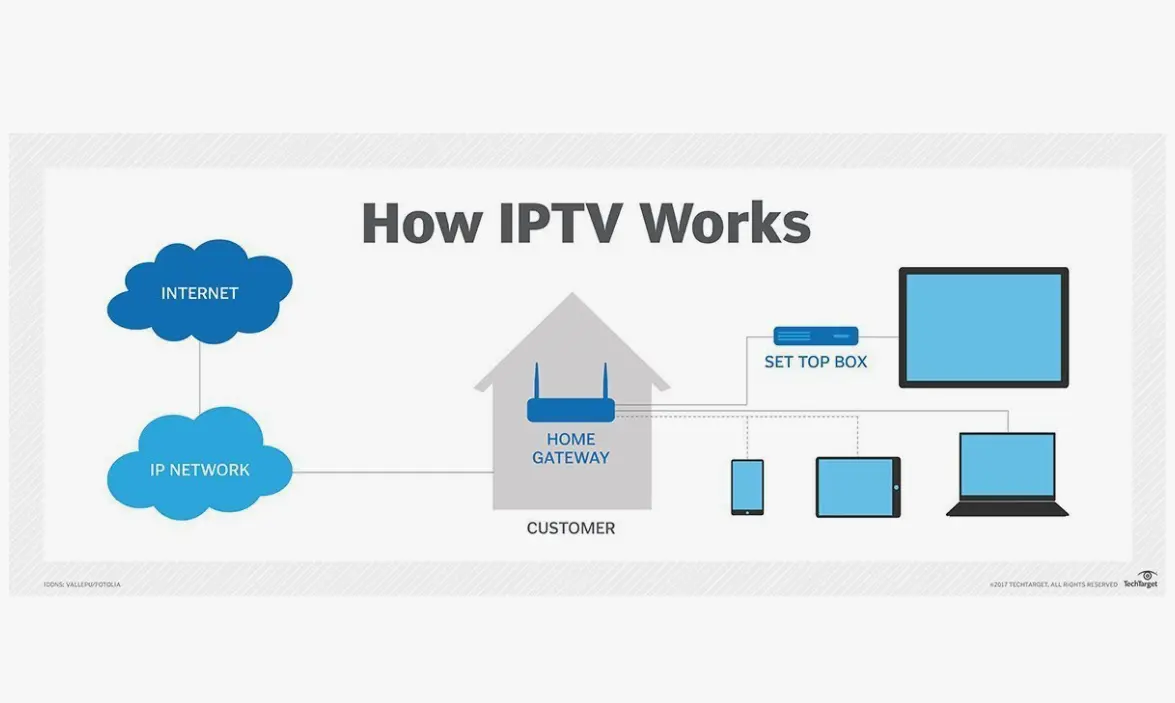
How Does IPTV Work?
At its core, IPTV works by transmitting video and audio data over the internet, using a broadband connection. This data is compressed and encoded into a digital format, which can then be streamed directly to a user’s device. Here’s a more detailed look at the process:
Content Acquisition: IPTV providers acquire content from various sources, including live TVa channels, video-on-demand libraries, and user-generated content platforms. This content is then prepared for delivery over the internet.
Encoding and Compression: The acquired content is encoded into a digital format, which is then compressed to reduce the file size. This compression is crucial for efficient streaming, as it allows high-quality video to be delivered over the internet without consuming excessive bandwidth.
Streaming: The compressed and encoded content is then transmitted over the internet to the end user. This transmission is done using a protocol called Internet Protocol (IP), which is the same protocol used for other types of data transmission over the internet.
User Interface: To access IPTV content, users typically use a set-top box, smart TV, or mobile app. These devices have built-in software that decodes the IPTV stream and displays it on the screen. The user interface allows users to browse available content, search for specific shows or movies, and interact with the service.
Middleware: Middleware is the software that connects the IPTV service with the end user’s device. It manages user authentication, billing, and content delivery, ensuring that the right content is delivered to the right user at the right time.
Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN is a network of servers that work together to deliver content to users. By distributing the content across multiple servers, a CDN ensures that the data travels the shortest distance possible, reducing latency and improving the quality of the stream.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: One of the key technologies used in IPTV is adaptive bitrate streaming. This technology automatically adjusts the quality of the video stream based on the user’s internet connection speed. If the connection is slow, the bitrate is reduced to prevent buffering; if the connection improves, the bitrate is increased to enhance video quality.
From Computer weekly
IPTV Infrastructure
IPTV relies on a complex infrastructure to deliver content seamlessly to users. This infrastructure includes:
Data Centers: IPTV providers use data centers to store and manage vast amounts of content. These data centers are equipped with high-performance servers that handle content encoding, storage, and distribution.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs play a critical role in ensuring that IPTV content is delivered quickly and reliably to users, regardless of their location. CDNs distribute content across multiple servers located in different geographic regions, which helps to minimize latency and buffering.
Middleware: Middleware acts as the bridge between the IPTV service and the end user. It handles tasks such as user authentication, billing, and content management. Middleware also provides the user interface that allows users to interact with the IPTV service.
Set-Top Boxes: Many IPTV users prefer to use set-top boxes to access content. These devices connect to the user’s television and provide a traditional viewing experience while offering the advanced features of IPTV, such as on-demand content and interactive TV.
Broadband Internet: A high-speed broadband internet connection is essential for IPTV. The quality of the viewing experience depends heavily on the speed and reliability of the user’s internet connection.
Types of IPTV Services
IPTV offers a range of services, each catering to different viewing preferences and needs. These services include:
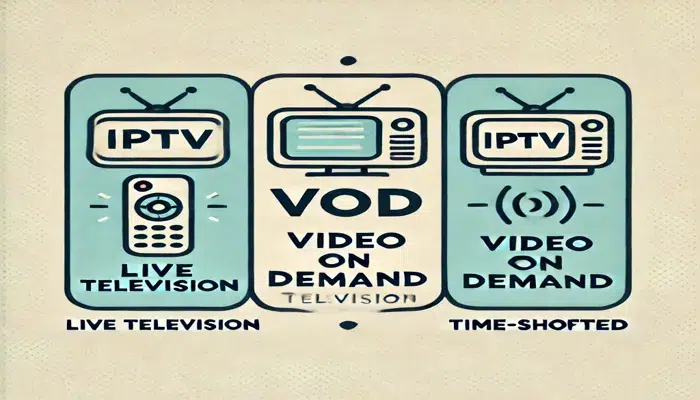
1. Live Television
Live television via IPTV allows users to watch live broadcasts of their favorite channels in real time. This service is similar to traditional TV but is delivered over the internet, offering additional features and flexibility.
Advantages of Live IPTV
-
- Global Access: Live IPTV offers access to a wide range of international channels, making it easy for users to stay connected with content from around the world. This is particularly beneficial for expatriates and multicultural households.
-
- Time-Shifted Viewing: Many IPTV providers offer time-shifted viewing options, allowing users to watch live content at a more convenient time. This feature is particularly useful for viewers who live in different time zones or have busy schedules.
-
- Interactive Features: Live IPTV often includes interactive features that enhance the viewing experience. For example, during a live sports event, users can access real-time statistics, participate in polls, or chat with other viewers.
2. Video on Demand (VoD)
VoD services allow users to choose from a library of movies, TV shows, documentaries, and other types of content. Users can watch this content at their convenience, with the ability to start, pause, rewind, and fast-forward through the content.
The Expanding VoD Library
The libraries offered by VoD services are vast and continually expanding. They include everything from the latest blockbuster movies to classic TV shows, independent films, and exclusive content not available elsewhere. This extensive selection is one of the main reasons why VoD has become so popular.
Personalization and Recommendations
One of the standout features of VoD is its ability to personalize the viewing experience. Many IPTV services use algorithms to analyze a user’s viewing habits and recommend content tailored to their preferences. This feature enhances user satisfaction by making it easier to discover new content that aligns with their interests.
3. Time-Shifted Media
Time-shifted media allows users to watch previously aired TV programs. This service is similar to VoD but is often limited to a specific time frame, such as the past week or month.
Catch-Up TV
Catch-up TV is a popular form of time-shifted media. It allows users to watch shows that have recently aired, typically within the last 7-30 days. This feature is particularly useful for viewers who have busy schedules and can’t always watch their favorite programs when they air.
Pause and Rewind Live TV
Some IPTV services also offer the ability to pause and rewind live TV. This feature is particularly useful for sports fans who want to re-watch key moments or for viewers who need to step away from the TV but don’t want to miss anything.
4. Interactive TV
Interactive TV is one of the most exciting aspects of IPTV. It allows users to interact with the content they are watching, adding a new dimension to the viewing experience.
Enhanced Viewing Experience
Interactive TV enhances the viewing experience by making it more engaging and personalized. For example, during a cooking show, viewers might be able to access recipes or purchase ingredients directly through their IPTV service. Similarly, sports fans could access real-time statistics and replays with the click of a button.
Social Integration
Many IPTV services integrate social media platforms, allowing users to share their viewing experiences with friends and family. This social integration makes watching TV a more communal activity, even when viewers are physically apart.
5. Over-the-Top (OTT) Services
OTT services are a subset of IPTV that refers to the delivery of content over the internet without the need for a traditional TV provider. Examples of OTT services include Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Hulu.
The Rise of OTT Platforms
OTT platforms have become increasingly popular in recent years, thanks to their convenience, affordability, and the quality of their content. These platforms have disrupted the traditional TV industry and have set new standards for what consumers expect from a television service.
Subscription Models and Monetization
Most OTT platforms operate on a subscription-based model, where users pay a monthly fee for access to the content. Some also offer ad-supported tiers, allowing users to access content for free in exchange for watching ads. This flexibility in pricing models has made OTT services accessible to a broad audience.
Description: This image explains the types of IPTV services, including features like Live TV, VoD, Time-Shifted Media, and Interactive TV.
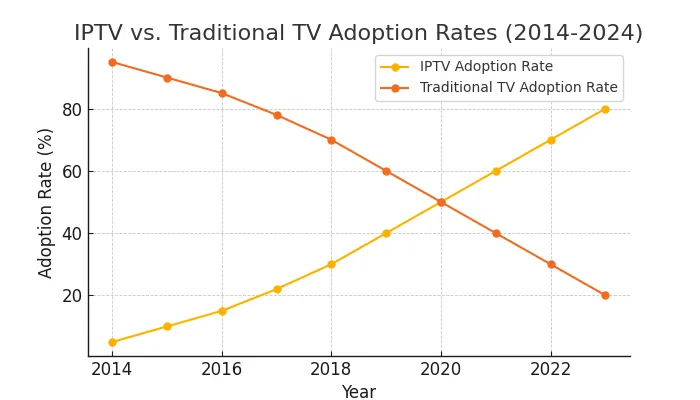
IPTV vs. Traditional TV A Comparative Analysis
As IPTV continues to gain popularity, it’s essential to understand how it compares to traditional TV. This section provides a comparative analysis of IPTV and traditional TV across several key factors.
1. Content Variety
-
- Traditional TV: Traditional TV typically offers a set number of channels, with content scheduled by the broadcaster. While some cable and satellite providers offer on-demand services, the selection is often limited.
-
- IPTV: IPTV provides a vast library of content, including live TV, VoD, and time-shifted media. Users have more control over what they watch and when they watch it.
2. Flexibility and Convenience
-
- Traditional TV: Viewers must adhere to the broadcaster’s schedule, which can be inconvenient. Recording shows for later viewing is possible but requires additional hardware like a DVR.
-
- IPTV: IPTV offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing users to watch content whenever they want. Features like pause, rewind, and catch-up TV add to the convenience.
3. Quality and Performance
-
- Traditional TV: Quality can vary depending on the provider and the viewer’s location. Satellite TV, for example, can be affected by weather conditions.
-
- IPTV: IPTV relies on a high-speed internet connection, so quality is generally consistent. HD and 4K content are readily available, and buffering is minimal with a reliable connection.
4. Cost
-
- Traditional TV: Cable and satellite TV can be expensive, especially when bundled with other services. Additional fees for premium channels, DVR service, and equipment rental can add up.
-
- IPTV: IPTV services are often more affordable, with flexible pricing models. Users can choose from various subscription plans, and there’s no need for additional hardware.
5. User Experience
-
- Traditional TV: The user experience is generally straightforward, but limited customization options mean that viewers are stuck with the broadcaster’s choices.
-
- IPTV: IPTV services often come with user-friendly interfaces, personalized recommendations, and interactive features that enhance the overall viewing experience.
6. Geographical Restrictions
-
- Traditional TV: Content is often region-locked, with certain channels or shows unavailable in specific areas.
-
- IPTV: IPTV can bypass geographical restrictions, allowing users to access content from around the world. This feature is particularly valuable for international audiences.
7. Customization and Personalization
-
- Traditional TV: Customization is minimal, with viewers largely confined to the broadcaster’s schedule and channel offerings. While DVRs offer some level of control, it is limited.
-
- IPTV: IPTV excels in customization and personalization. Users can create their own playlists, set reminders for their favorite shows, and receive recommendations based on their viewing habits. This level of control enhances the overall viewing experience, making it more tailored to individual preferences.
8. Environmental Impact
-
- Traditional TV: The production, distribution, and consumption of traditional TV require significant physical infrastructure, including cables, satellite dishes, and broadcasting towers. This infrastructure has an environmental impact, particularly in terms of energy consumption and resource use.
-
- IPTV: IPTV is more environmentally friendly as it leverages existing internet infrastructure. While data centers that support IPTV do consume energy, advances in technology are making them increasingly efficient. Additionally, IPTV reduces the need for physical media, such as DVDs, further minimizing environmental impact.
The Future of IPTV
The future of IPTV is bright, with numerous technological advancements set to enhance the service even further. Here are some trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of IPTV:
1. 5G Technology
The rollout of 5G networks will have a significant impact on IPTV. With faster internet speeds and lower latency, 5G will enable even higher-quality streaming, including 8K resolution and virtual reality content. It will also make IPTV more accessible in areas where broadband internet is currently unavailable.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning will play a crucial role in personalizing the IPTV experience. By analyzing viewing habits, these technologies can recommend content tailored to individual preferences, create personalized playlists, and even predict what users want to watch before they know it themselves.
3. Augmented and Virtual Reality
As AR and VR technologies continue to develop, they will likely be integrated into IPTV services. This integration could lead to immersive viewing experiences, such as watching a sports event as if you’re in the stadium or exploring a movie set in 360 degrees.
4. Increased Interactivity
The interactive features of IPTV are set to become even more advanced. Future developments might include multi-angle viewing options, where users can switch between different camera angles during a live event, or interactive storytelling, where viewers can influence the plot of a show.
5. Expansion of Content Libraries
As competition among IPTV providers intensifies, content libraries will continue to expand. Exclusive content, such as original series and movies, will become a key differentiator, with providers investing heavily in production to attract and retain subscribers.
6. Globalization of Content
IPTV has already begun to break down geographical barriers, and this trend will continue. Providers will increasingly offer content tailored to international audiences, with more language options, subtitles, and region-specific content.
7. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology could revolutionize the IPTV industry by providing a more secure and transparent way to manage content rights and payments. By using blockchain, IPTV providers can ensure that content creators are fairly compensated for their work and that users have access to authentic and authorized content.
8. Sustainability Initiatives
As environmental concerns become increasingly important, IPTV providers may adopt more sustainable practices. This could include using renewable energy to power data centers, reducing the carbon footprint of content delivery, and promoting digital rights management (DRM) solutions that reduce the need for physical media.
Challenges Facing IPTV
While the future of IPTV is bright, several challenges must be addressed to ensure its continued growth and success:
1. Network Infrastructure
The quality of the IPTV experience depends heavily on the user’s internet connection. In regions with poor network infrastructure, users may experience buffering, lag, or reduced video quality. As IPTV adoption increases, there will be a greater need for robust and reliable broadband networks.
2. Content Licensing
Content licensing remains a complex issue for IPTV providers. Securing the rights to stream content, especially internationally, can be challenging and expensive. Providers must navigate these challenges to offer a diverse and appealing content library.
3. Piracy and Security
Piracy is a significant concern in the IPTV industry. Unauthorized streams of live TV and VoD content can lead to revenue loss for providers and content creators. Additionally, security issues such as hacking and data breaches pose a threat to both providers and users. Ensuring secure and legal content delivery will be crucial for the industry’s long-term viability.
4. Regulatory Hurdles
The regulatory environment for IPTV varies by country, and changes in legislation could impact the industry’s growth. Providers must stay informed of regulatory developments and adapt their business models accordingly.
5. Competition from OTT Platforms
While IPTV and OTT platforms share many similarities, they are also competitors. As OTT platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime continue to grow, IPTV providers will need to differentiate themselves by offering unique features, exclusive content, and competitive pricing.
6. Consumer Awareness and Education
Many consumers are still unfamiliar with IPTV and how it differs from traditional TV and OTT services. Educating potential users about the benefits of IPTV, how to set it up, and what to expect from the service is essential for driving adoption. Providers must invest in marketing and customer support to help users make the transition to IPTV.
How to Choose the Right IPTV Service
With so many IPTV services available, choosing the right one can be daunting. Here are some factors to consider when making your decision:
1. Content Library
The content library is arguably the most important factor when choosing an best IPTV service. Consider what types of content are most important to you—whether it’s live TV, VoD, international channels, or exclusive series—and choose a service that offers a robust selection in those areas.
2. User Interface
A user-friendly interface can significantly enhance your viewing experience. Look for services with intuitive navigation, easy-to-use search functions, and personalized recommendations.
3. Device Compatibility
Ensure that the IPTV service you choose is compatible with your devices. Whether you prefer to watch on your TV, computer, tablet, or smartphone, the service should be accessible across all your preferred platforms.
4. Quality and Performance
Check the quality and performance of the service, including the resolution of the streams, buffering times, and overall reliability. Reading reviews from other users can provide valuable insights into the service’s performance.
5. Pricing and Plans
Consider the pricing and subscription plans offered by the IPTV service. Some services offer flexible plans, allowing you to pay only for the content you want, while others may offer a flat rate for access to all content. Compare prices and choose a service that fits your budget.
6. Customer Support
Good customer support is essential, especially if you encounter issues with your service. Look for providers that offer 24/7 support and multiple contact methods, such as phone, email, and live chat.
7. Trial Periods
Many IPTV services offer free trials or money-back guarantees, allowing you to test the service before committing to a subscription. Take advantage of these offers to ensure the service meets your needs.
8. Reputation and Reviews
Before committing to an IPTV service, research its reputation and read reviews from other users. Pay attention to feedback about the service’s reliability, content quality, and customer support. A provider with a strong reputation is more likely to deliver a positive experience.
Conclusion
IPTV is revolutionizing the way we consume television content. With its flexibility, extensive content libraries, and innovative features, it’s no wonder that more and more viewers are making the switch from traditional TV. As technology continues to advance, IPTV will likely become even more integral to our entertainment landscape, offering new ways to engage with and enjoy the content we love.
For those considering making the switch to IPTV, the key is to choose a service that aligns with your viewing habits and preferences. Whether you’re a sports fanatic, a movie buff, or someone who enjoys international programming, there’s an IPTV service out there for you.
The future of television is here, and it’s digital. IPTV is not just a trend; it’s a transformative force that is reshaping the industry. As it continues to evolve, it will offer even more exciting opportunities for viewers and content creators alike. Embrace the future of television and explore the world of IPTV today.